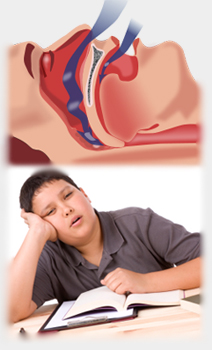
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is the most prevalent sleep-breathing disturbance, affecting
24% of men and
9% of women in the general population
[1,2].
An estimated
82% of men and 92% of women with moderate-to severe OSA have not been diagnosed.
Sleep Apnea Events
as a complete cessation of breathing (apnea) or a marked reduction in airflow (hypopnea) during sleep, and are considered clinically relevant if they last more than 10 s. The episodes of apneas and hypopneas may persist for 30-60s in some individuals.
Obstructive Sleep Apnea
- repetitive obstruction of the upper airway often resulting in oxygen desaturation and arousals from sleep
- excessive daytime sleepiness
- unrefreshing sleep
- poor concentration
- fatigue
OSA is a serious condition that diminishes quality of life and is also associated with many common comorbid conditions.
Studies have shown that patients with OSA will have an increased incidence of:
- coronary artery diseases
- hypertension
- congestive heart failure
- cerebrovascular accidents
- gastroesophageal reflux disease
It is estimated that the
average life span of a patient with untreated OSA is 58 years, much shorter than the average life span of 78 years for men and 83 years for women.
- Kryger MH. Diagnosis and management of sleep apnea syndrome.
Clin Cornerstone 2000; 2:39 - 47
- Young T, Hutton R, Finn L, et al. The gender bias in sleep apnea diagnosis. Are women missed because they have different symptoms?
Arch Intern Med 1996; 156:2445 - 2451